|
In the skies above Berlin The GSW
office block
by
sauerbruch hutton architects
|
|
|
Home |
Case Study Index |
|
||||
| Concept |
Energy Concept |
Structure | ||
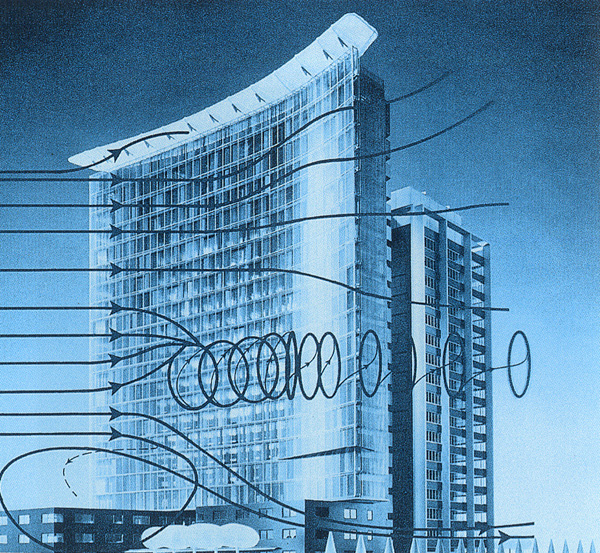
| Many new German buildings have lessons to teach about energy efficiency, but the jury was impressed with the originality of the scheme’s strategy. This construction, which has been highly-praised by the specialist press, is also impressive as a result of its multi-functional interior. Its foyer, atrium and conference rooms all reveal new directions as regards interior design and office architecture. This also applies to a well-thought-out low energy concept, which reduces | |
| consumption by up to 40% via an ingenious fresh air/outgoing air thermal current with temperature storage. A double glass facade system, which is unique in technical engineering terms, ensures clean interior air and optimal exploitation of natural light. A thermal flue is created in the double west wall of the slab block which spans the two main low-rise blocks; its plan is narrow to maximize daylight use and natural ventilation; the facade is carefully shaded to reduce solar heating in summer, and a ‘wind roof’ assists natural ventilation. In winter, the mechanical ventilation system feeds back heat from exhaust air to the central plant. At a height of 81 meters, the office construction is crowned by a wind sail, which, at the same time, is also a vital component of the energy concept. |

|
| b. Buffer Zones | |
| c. Effective solar protection | |
| d. Cross-ventilation | |
| e. Heat recovery | |
| f. Thermal mass | |
|
| Home | Case Study Index | |